Investigation of the Covid-19 Pandemic Status in Guangdong Province after the Optimization of Pandemic Prevention and Control Measures at the End of 2022 Based on Optimized Transmis...
2023-05-201087When the Omicron strain was dominant, one or more peaks occurred in most countries after the pandemic control measures was relaxed. Considering the dynamic clearing and optimized control measures adopted by China, the SKLRD team used the improved SEIR-CD transmission dynamics model to predict the development trend of COVID-19 in Guangdong province and Guangzhou city, providing a scientific basis for the development of anti-pandemic measures.
The research findings of the research have recently been published in the international medical journal Journal of Thoracic Disease with the title of “Real-time assessment of COVID-19 epidemic in Guangdong Province, China using mathematical models.” The team used the daily number of COVID-19 infections reported by the National Health Commission of China from October 22 to November 20 of 2022 to calculate the transmission rate of BA.5.2 based on EpiEstim (89%), further considering the average transmission period of 5.2 days, and adding two parameters of the rate of severe cases (0.2%) and mortality rate (0.036%) to establish the optimized model of SEIR-CD transmission dynamics (Figure 1) and explore the COVID-19 outbreak in Guangdong Province after the adoption of optimized pandemic prevention and control measures at the end of 2022. In order to achieve reasonable allocation of medical resources, the current SEIR-CD model added the critically ill population (Critical, C) and dead population (Death, D) on the basis of SEIR, in combination with the actual local rate of severe cases and mortality rate. As a result, the model can be used to work out the changing trend of the numbers of severe cases or deaths and greatly improve its practicability in pandemic prediction.
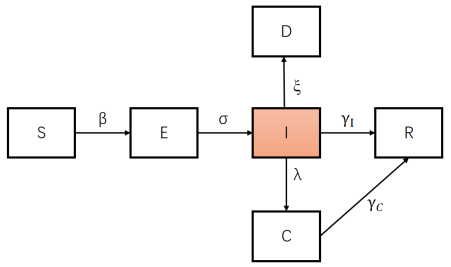
Figure 1. The optimized SEIR-CD transmission dynamics model
According to the research finding (Figure 2), the current round of outbreak in Guangdong is expected to peak from December 21 to 25, 2022, with about 14.98 million people infected on the day. From December 24 to 26, 2022, the cumulative number of infections will reach about 70 percent of the province’s population. Existing severe cases are expected to peak around January 1 to 5, 2023, and at the peak, the number of severe cases will be about 101,450.
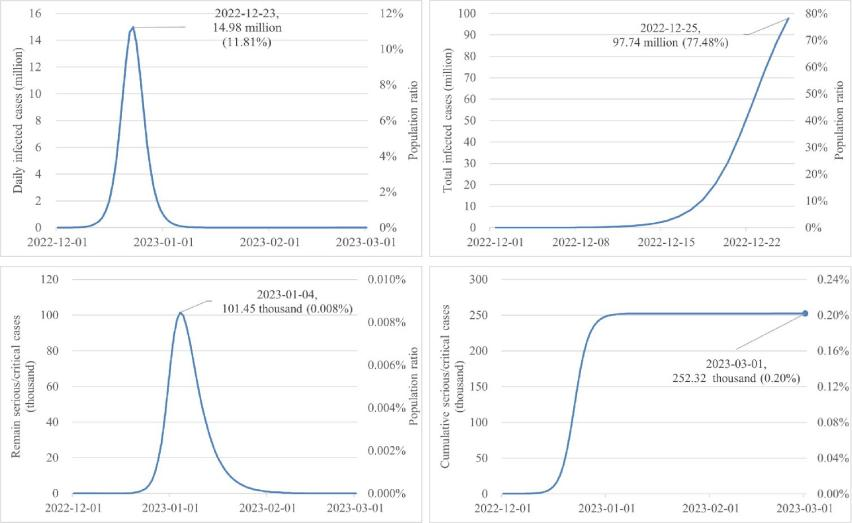
Figure 2. The COVID-19 pandemic results in Guangdong Province
The current round of outbreak in Guangzhou (Figure 3) is expected to peak from December 22 to 23, 2022, with a peak number of about 2.45 million new infections. From December 24 to 25, 2022, the cumulative number of infections will account for about 70% of the city’s total permanent resident population. The number of existing severe cases is expected to peak around January 4 to 6, 2023, with the number of existing severe cases at about 6,320.
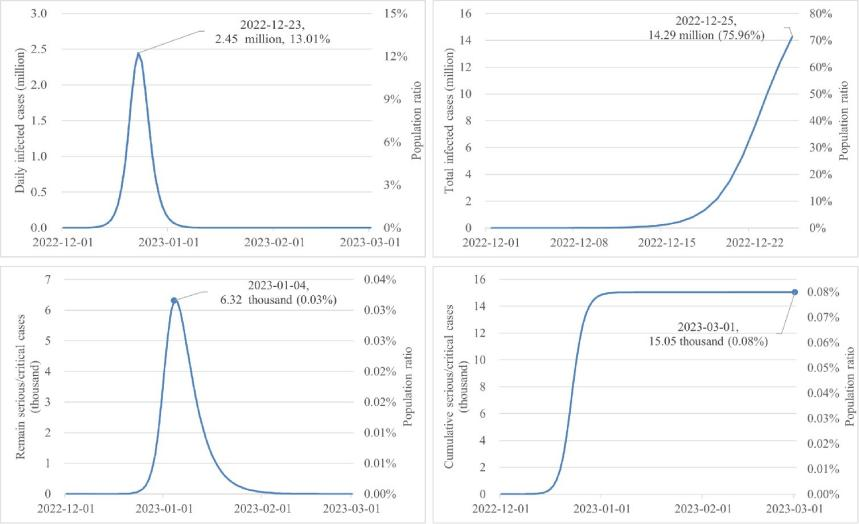
Figure 3. Results of the COVID-19 pandemic in Guangzhou
After the adoption of optimized pandemic prevention and control measures, the SEIR-CD model predicts that by December 25, 2022, the cumulative number of infections in Guangdong province will reach about 70% of the province’s population, while that in Guangzhou will reach 70% of the city’s total population by December 23, 2022. The results are more in line with the monitoring status of the Guangdong Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Based on the statistical data of Covid-19 pandemic in 22 developed countries or regions in 2022, the average duration between two infection peaks in these countries or regions is 149.35 days (median: 161 days), the average number of new cases of the second peak is 48.61% of that of the first peak (median: 41.72%), which may be due to the decay effect of antibodies. Our team speculated that there will be a minor outbreak in the next stage, possibly in May-June 2023.