Meta-analysis Finds that the Efficacy of COVID-19 Serological Tests Declines in the Early-Stage Disease
2021-06-11951Professor Li Jing’s team from the lab and Professor Wen Weiping from the Department of Otorhinolaryngology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, published their research result “Clinical application of detecting IgG, IgM or IgA antibody for the diagnosis of COVID-19: a meta-analysis and systematic review” on journal International Journal of Infectious Diseases in January, 2021, providing comprehensive proofs for the actual clinical application of COVID-19 serological testing. Timely detection and quarantine are critical to prevent spread of disease. Nucleic acid testing is the gold standard for diagnosing COVID-19, while serological testing is important for diagnosing COVID-19.
This meta-analysis includes 68 research items, focusing on diagnostic test performance of COVID-19 including various combinations of antibodies like IgG antibodies, IgM antibodies and IgA antibodies, which finds that IgG or IgM is the best in terms of diagnostic efficiency, with 79% of sensitivity and 98% of specificity. In addition, compared with the test performed earlier after the onset of symptoms, the serological test performed 2 weeks after the onset of symptoms shows higher diagnostic accuracy. The use of S protein or S and N proteins as antibodies to prepare antigens can also help improve diagnostic accuracy.
For the first time, this research puts forward the IgG combined with lgM diagnostic reagents should be used to assist in the diagnosis or screening of COVID-19 infections, and it was found that the early diagnostic efficacy of serological tests was limited, providing important, comprehensive evidence for the production requirements of diagnostic reagents and clinical applications.
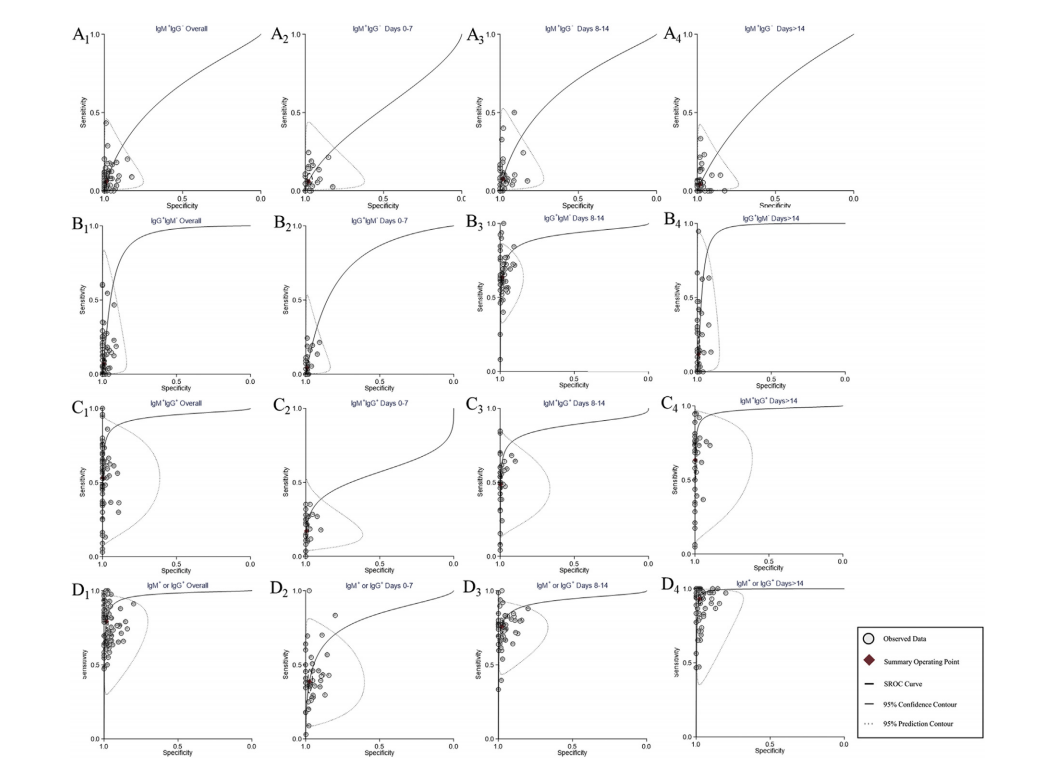
The characteristic curve of IgM antibody combined with IgG antibody. (A) IgM+IgG-; (B) IgG+IgM-; (C) IgM+IgG+; (D) IgM+ or IgG+. A1-D1, antibodies are detected, and the detection time is not stratified. A2-D2, antibodies are detected 0-7 days after the onset of symptoms. A3-D3, antibodies are detected 8-14 days after the onset of symptoms. A4-D4, antibodies were detected >14 days after the onset of symptoms.