Professor Zhang Xiaowen’s research team makes new progress in the field of MUC1 research
2022-02-17917Recently, the research team led by Professor Zhang Xiaowen with SKLRD’s Allergic Lung Disease Group has published a research titled “MUC1 deficiency induces the nasal epithelial barrier dysfunction via RBFOX3 shortage augment ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation in allergic rhinitis pathogenesis” in Allergy (IF=13.14), an international authoritative journal in allergy and allergic reaction.
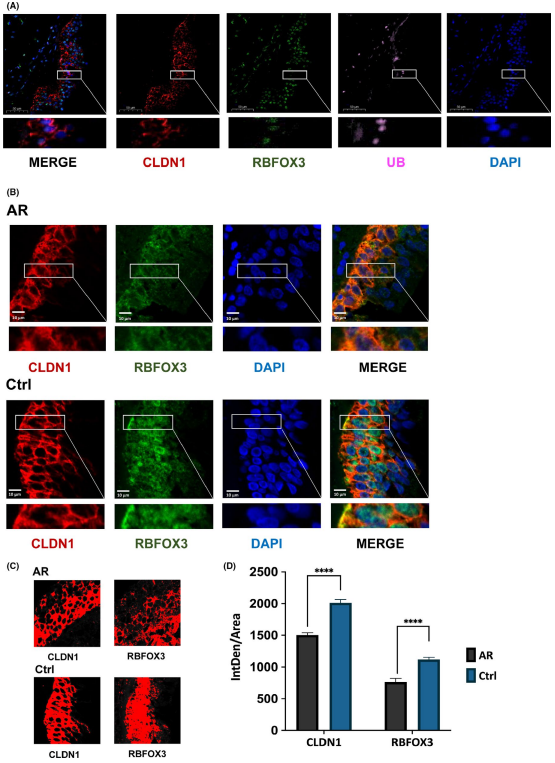
The CLDN1 expression and RBFOX3 expression levels declined in the nasal mucosa of patients with allergic rhinitis, as compared with healthy controls
The research results revealed that RBFOX3-deficient nasal epithelial cells were observed in patients with allergic rhinitis (AR) compared with healthy controls, and that CLDN1 and RBFOX3 expression were significantly down-regulated in the nasal mucosa of AR patients. It was speculated that CLDN1 ubiquitination regulated by RBFOX3 was involved in MUC1-mediated AR pathogenesis. Further in vivo experiments showed that in a mice model of AR developed using nasal administration of the ubiquitin-proteasome inhibitor MG132, the expression levels of CLDN1 and RBFOX3 increased significantly, and the disease symptoms and nasal inflammation were significantly improved in the mice. In conclusion, MUC1 deficiency further inhibited CLDN1 expression through down-regulation of RBFOX3 expression for enhancing ubiquitin-proteasome degradation in the AR. Furthermore, MG132 nasal administration also alleviated AR by reducing physical barrier dysfunction in the nasal epithelium.
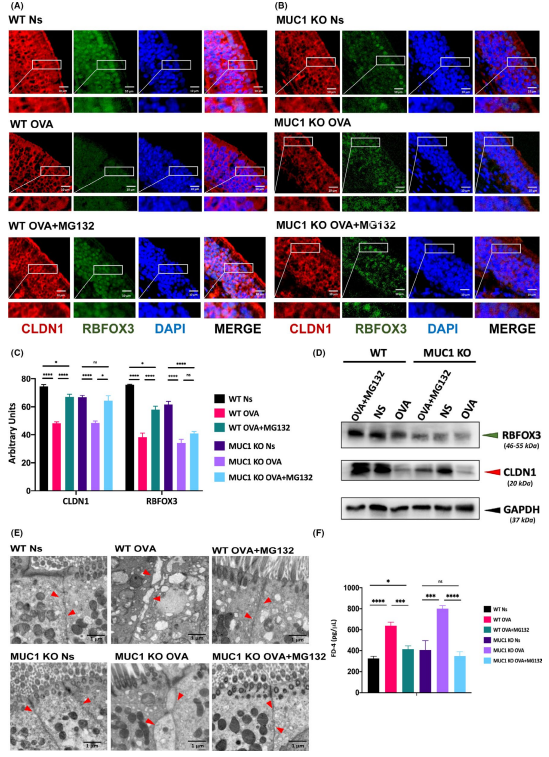
Role of MG132 nasal administration in the nasal mucosa of AR mice