Professor Sun Baoqing’s team publishes the variation trend of antibody titer of the domestic COVID-19 inactivated vaccine booster
2022-03-111549Recently, the team led by Professor Sun Baoqing from the National Center for Respiratory Medicine, the State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Diseases, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University and the Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Health has published the latest research results of antibody immunity surveillance after receiving the injection of domestic COVID-19 inactivated vaccine in the international academic journal Allergy (IF = 13.1). In the article titled “Humoral immune response of BBIBP COVID-19 vaccination before and after the booster immunization”, the researchers revealed the trend of antibody titer after receiving the booster injection, providing positive reference data for the safety and effectiveness of Sinopharm vaccine, and providing a reliable and fundamental basis for the development of a safe and efficient COVID-19 vaccine. Dr. Cheng Zhangkai, Huang Huimin, Zheng Peiyan, and Xue Mingshan with the laboratory are the co-first authors of this study, and Professor Sun Baoqing is the corresponding author.

Background
As COVID-19 epidemic was spreading in an explosive trend around the world, efficient and safe vaccination has become an effective prevention means to reduce infection and fatality rate. As the protective efficacy of vaccines may gradually decrease over time, it has become an important task and trend in the pandemic prevention measures under the current stage in response to the emergence of different virus variant strains and the urgent demand of the public for strengthening the immune effectiveness. Since the promotion of booster injection is still under an initial stage, the studies on the enhanced antibody immune effect and changes of antibody level are still not clear. In this study, our team reported the dynamics, persistence and neutralization ability of BBIBP vaccine-induced immunity, as well as the enhanced antibody response triggered by booster injections, to solve the key issues of how vaccine-induced specific antibody levels and antibody neutralization ability change during BBIBP vaccination. It provides reliable basis for the research and development of COVID-19 vaccine.
Research objects and method
This study was carried out by several organizations in cooperation (the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medial University, the Fifth (Zhuhai) Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, the Eighth People’s Hospital of Dongguan), involving a total of 353 healthy adult participants (106 men, 247 women) to complete the whole study, whose age range is 20-74 (median: 33). The above participants’ inclusion are strictly in accordance with the relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria. Participants were sampled and tested for corresponding antibody levels and neutralizing antibody tests at 7 points of time.
Results
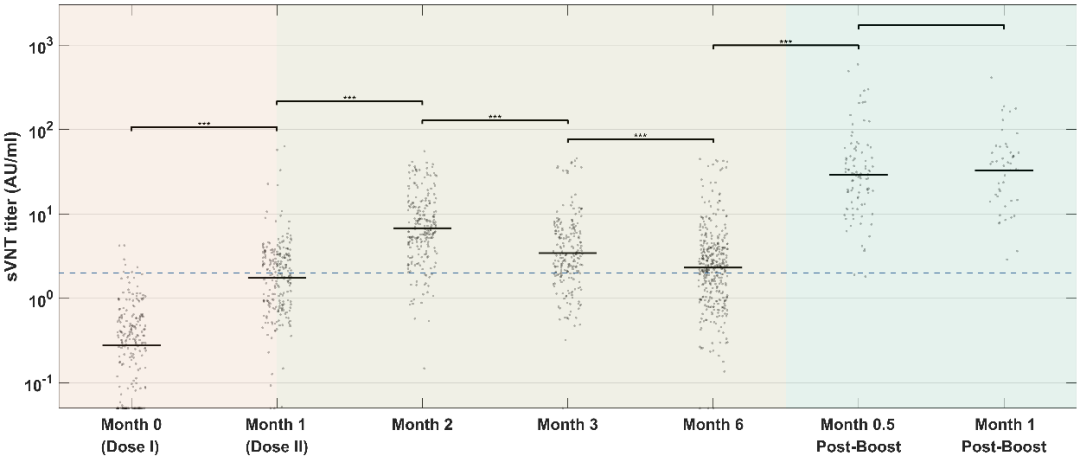
According to the study, throughout the vaccination process, the titer of the virus-specific antibodies SARS-CoV-2-IgG / IgA / IgM peaked in the second month after the first injection, and then slowly decreased. Interestingly, the results showed that the levels of SARS-CoV-2-IgG and neutralizing antibodies (sVNT) changed most significantly (P <0.05) one month after receiving the booster injection, and the trends of the two were highly consistent (Figure 1). Compared with other antibodies, the titer of SARS-CoV-2-IgA monitored in the seven points of time remained at a relatively constant low level (Figures 2a-c).
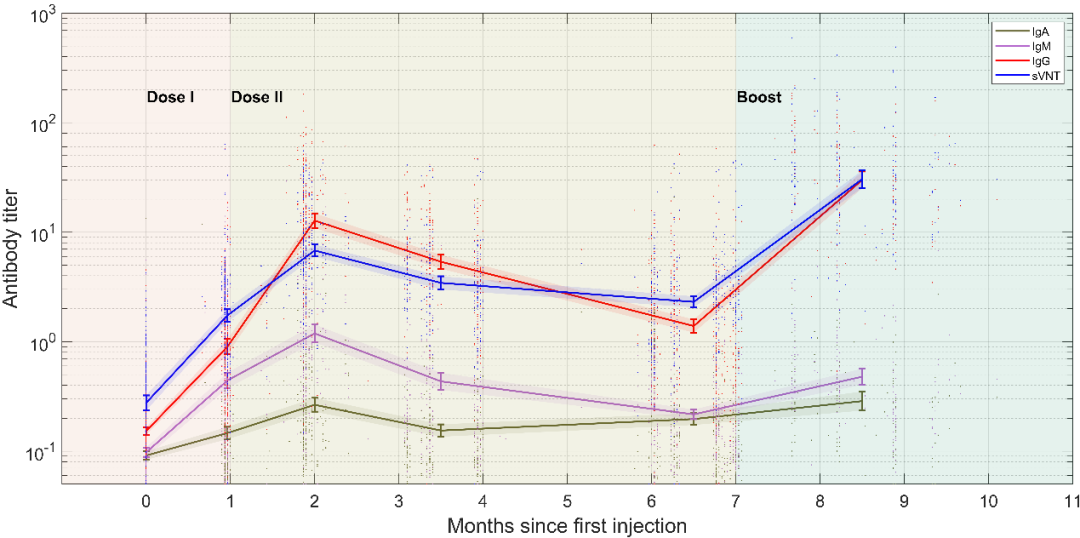
Figure 1: Antibody levels monitored at multiple points of time. IgA (green), IgM (purple), IgG (red), sVNT (blue)
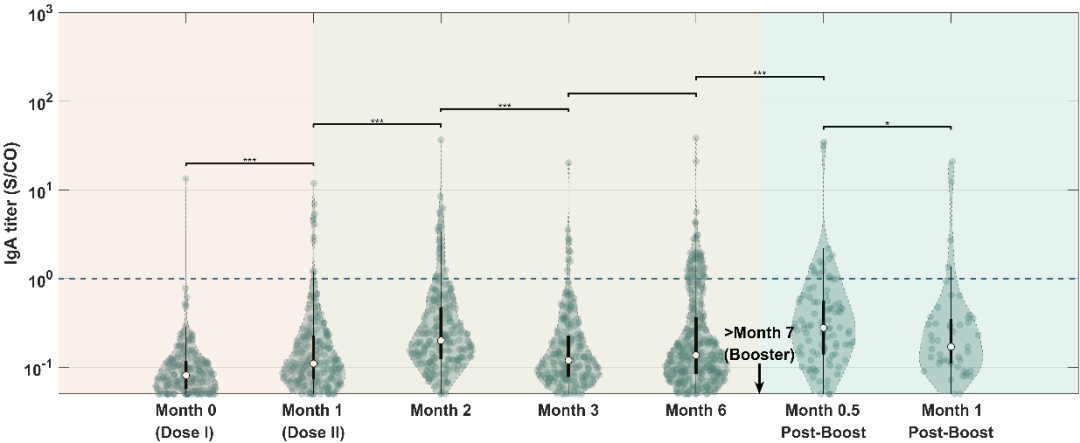
a
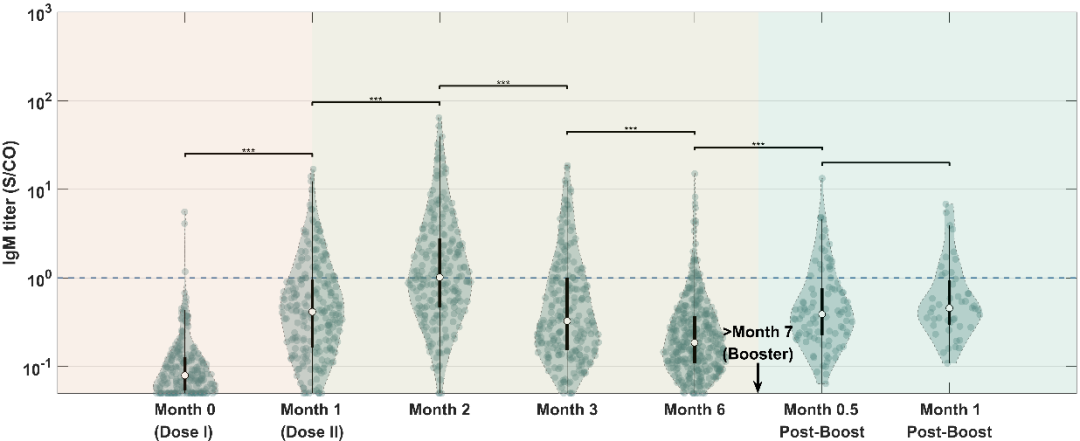
b
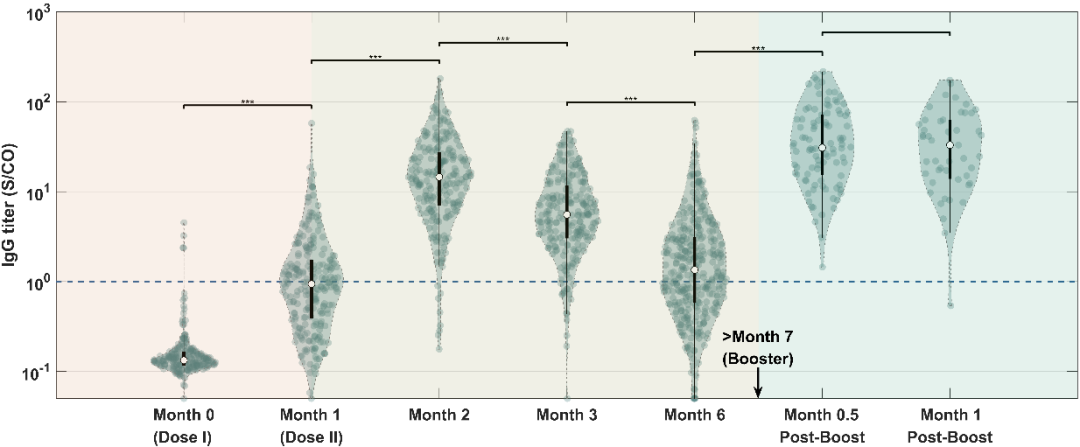
c
Figure 2. Titer monitoring of relevant antibodies at each point of time.(a) IgA.(b) IgM.(c) IgG.
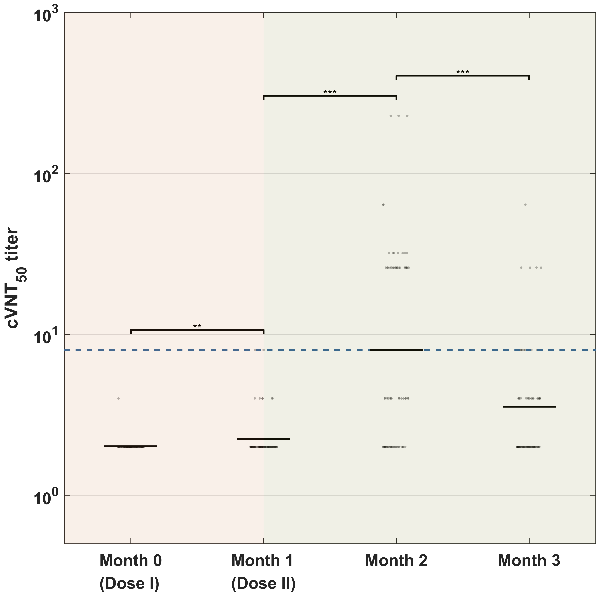
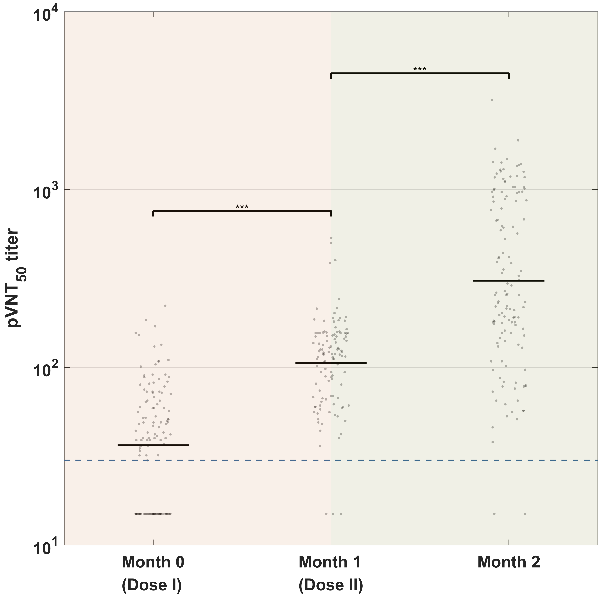
It was found that the corresponding neutralizing titer changes showed a significant upward trend after the completion of two injections. Notably, the titer of the sVNT significantly increased 0.5 month after receiving the booster injection, which was 13.2 times higher than that in the sixth month, and 4.5 times that of the first peak (Figures 3a-c).
a
b
c
Figure 3. Virus neutralization test results at different points of time.
(a) True virus neutralization experiment. (b) Pseudovirus neutralization experiment.(c) Substitute virus neutralization experiment.
This study further grouped the participants by age (i. e., 40 and> 40 years) and gender and compared changes in antibody levels at each monitoring point. The results showed that changes of antibody titer levels were consistent among different age groups and genders. Also, the measured titer level of SARS-CoV-2-IgG was correlated with that of sVNT (r = 0.647, P <0.001).
Views
By exploring the relevant researches on vaccine titer under the current stage, the researchers found that all the evidences showed a declining trend in long-term protection of vaccines over time. However, in addition to induced neutralizing antibody, whether other levels of vaccine protection have any positive effect depends on the formation of immunologic memory. Related studies show that immunity against SARS-CoV-2 aroused by a third dose of the inactivated vaccine helps to provide better immune protection and enhanced neutralizing titer.
This study monitored the humoral responses induced throughout the vaccination process, such as virus-specific antibodies (SARS-CoV-2-IgA / IgM / IgG), and performed viral neutralization test. The results showed that the persistence and neutralization titer of the immunity induced by vaccines declined over time, in addition to monitoring the strong memory antibody response after receiving the booster injection, which thus demonstrated the significant immune effect of the booster injection. It was found that SARS-CoV-2-IgG was mainly responsible for neutralization titer during humoral immunity, suggesting its critical role in protecting the human body from viral invasion. Interestingly, the changes in SARS-CoV-2-IgM were quite different from the other two types of antibodies, triggering similar titer with that in the first injection after the booster injection, which was consistent with the features observed in the absence of memory immunity. This research work laid the foundation for the clinical application of inactivated vaccine booster injection. More real-world studies with large-scale outbreaks are needed in the future to comprehensively assess the immune efficacy of inactivated vaccines and to determine the neutralizing antibody thresholds for preventive diseases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study found that the immune efficiency of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine BBIBP-CorV in healthy adults boasted excellent tolerance and safety, while the humoral immune response was effectively induced after receiving the first two doses and peaked two months after the initial injection, and then gradually declined over time. In addition, the booster injection significantly induced memory immunity, in which the neutralizing titer reached 13.2 times one month after the booster injection. It can be concluded that the current vaccine strategy plays a positive role in improving the immune effectiveness of the masses. In addition, the advantage of the booster injection has brought good news to the further consolidation of the immunogenicity of novel coronavirus and its variant strains.
China has recently officially deployed the sequential booster vaccination with various types of COVID-19 vaccines, and is looking forward to more relevant studies to serve the global fight against the Covid-19.