The research team led by Professor Lu Wenju achieves new progress in the research of pathogenesis of lung fibrosis
2022-07-151445Recently, the research team led by Professor Lu Wenju from SKLRD’s COPD and pulmonary vascular disease group has published a research titled “Bone morphogenetic protein 4 inhibits pulmonary fibrosis by modulating cellular senescence and mitophagy in lung fibroblasts” in the international authoritative journal European Respiratory Journal (IF=33. 795) .
Pulmonary fibrosis is a class of progressive, fatal lung diseases, among which the commonest and most severe one is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The average survival period of patients after diagnosis is only 3-5 years . The accumulation of myofibroblasts is crucial in the development of IPF. Fibroblast aging and insufficient mitophagy deficiency promote their differentiation into myofibroblasts, thus promoting the development of IPF. Bone-forming protein 4 (BMP4) is a multifunctional growth factor that is critical in the early stages of lung development, but its role in the development of lung fibrosis has remained unclear.
This paper found that the amount of BMP4 expression was significantly reduced in the lung tissue and fibroblasts of IPF patients and BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis mice. Moreover, the absence of BMP4 gene aggravated the BLM-induced lung fibrosis, and the over-expression of BMP4 could significantly improve the BLM-induced lung fibrosis. In terms of mechanism, this paper found that BMP4 can inhibit the activation of TGF-1-Smad2 / 3 signaling pathway, and inhibit fibroblast aging and mitophagy deficiency, thus inhibiting the differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, and ultimately playing a protective role in the occurrence and development of lung fibrosis.
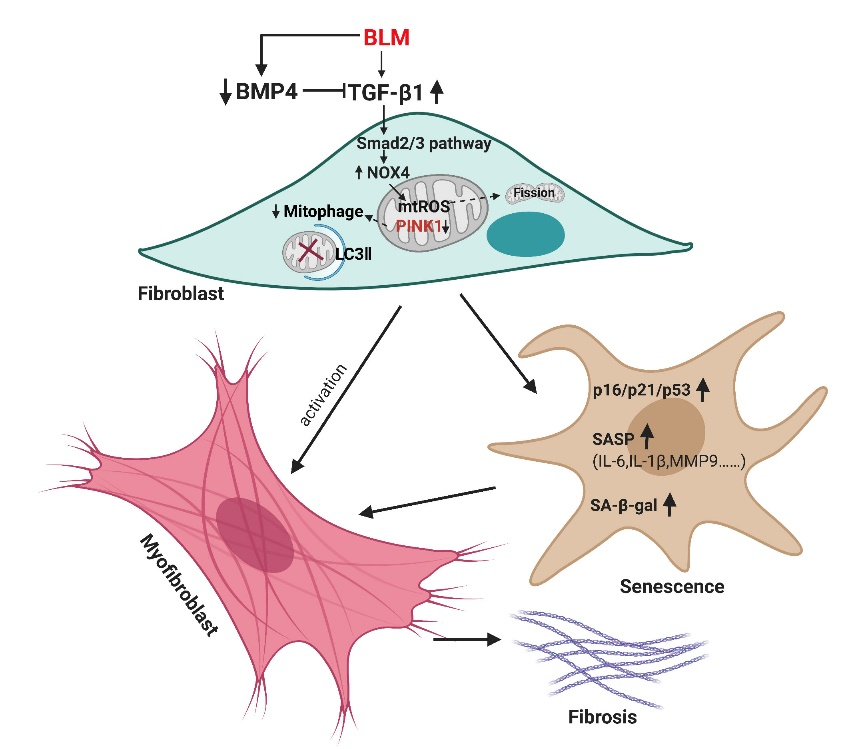
Schematic diagram of the mechanism of BMP4 in regulating the development of pulmonary fibrosis